GENETIC ENGINEERING
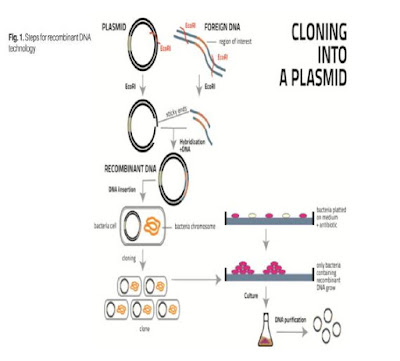
GENETIC ENGINEERING The method of changing inherited characteristics of an organism by altering its genetic material is called genetic engineering. It is also known as Recombinant DNA technology. Recombinant DNA technology is the technique, which allows DNA to be produced via artificial means. The procedure has been used to change DNA in living organisms and may have even more practical uses in the future. It is an area of medicine, which is at present in its initial phase of the overall concerted effort. The cornerstone of most molecular biology technologies is the gene. To facilitate the study of genes, they can be isolated and amplified. One method of isolation and amplification of a gene of interest is to clone the gene by inserting it into another DNA molecule that serves as a vehicle or vector that can be replicated in living cells. When these two DNAs of different origin are combined, the result is a recombinant DNA molecule. 1. TOOLS OF GENETIC ENGINEERING The tools of...
